Microsoft Introduces Windows 10?

Microsoft Today at its conference in San Francisco Announce the anticipated Next Step in it's iteration of Operating Systems.
No it Is Not Windows One, not WindowsTH, Windows X Nor even Windows 9.
Windows have thrown an egg on the face of an Army of rumoured towards its next Operating Systems Name to Finally announce its next Generation of Operating System as Windows 10.
Boasting an announcement of over 1.5 Billion Users of Globally, Microsoft Takes its Unified "One product family. One platform. One store" Philosophy. A Philosophy Microsoft has tested with the largely unliked Windows 8 iterations.
Joe Belfiore noted of future transitions, "We want all these Windows 7 users to have the sentiment that yesterday they were driving a first-generation Prius, and now with Windows 10 it's like a Tesla." a statement which no doubt is testament to the Vision of Where Windows Priorities lie.
Some of Windows 10 Preliminary Features include:
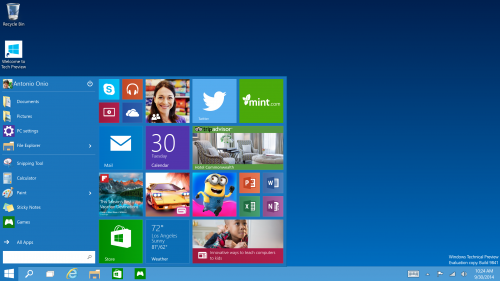
The Start Menu - Windows 7 users will buzz with pride to know that Windows 10 comes with a familiar start menu while Mobile User will find it Great that it is re-sizable with live tiles and your favorite apps.
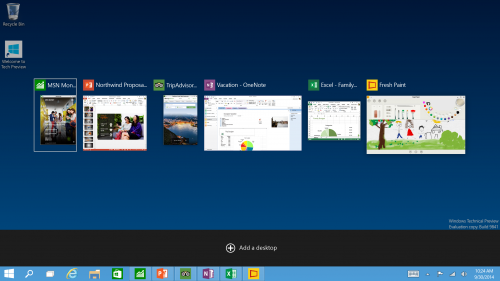
New Task View Button - There’s a new task-view button on the taskbar for quick switching between open files and quick access to any desktops you create.
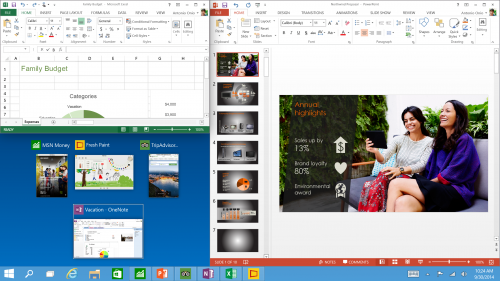
Snap Enhancements - You can now have four apps snapped on the same screen with a new quadrant layout. Windows will also show other apps and programs running for additional snapping and even make smart suggestions on filling available screen space with other open apps.
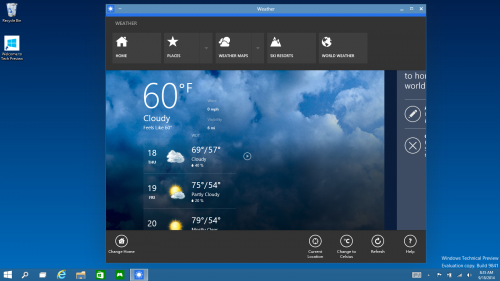
Everything Runs in Windows - The Operating System is afterall called "Windows", So Sticking to its Root, Windows Apps from the Windows Store now open in the same format that desktop apps do and can be resized and moved around, and have title bars at the top allowing for maximize, minimize, and close with a click.
Finding Files and Searching the Web Fast - File Explorer now displays your recent files and frequently visited folders making for finding files you’ve worked on is easier.
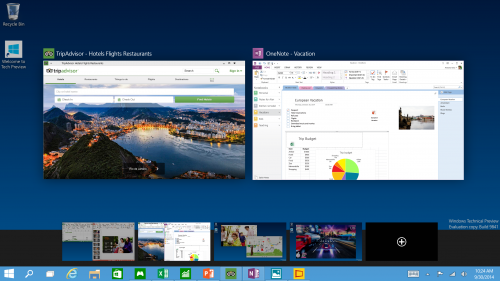
Multiple Desktops - Makes it very easy to compartmentalize/create section for different purposes or projects and quick switches between these desktops easily picking up where you left off on each desktop.
Its expected that the final product will see the addition of other useful features as the product develops further. Windows 10 is slated to ship at some point within mid-2015.
Microsoft says the technical preview of Windows 10 for PCs will come out on Wednesday and will be available at Preview.Windows.com. Here is an introduction of the Windows Insider Program for Windows 10:
Source: http://blogs.windows.com/bloggingwindows/2014/09/30/announcing-windows-10/